Land Use
The UK Digital Twin supports queries across number of aspects of the UK energy related infrastructure, including the electrical power system, the gas transmission system and land use.
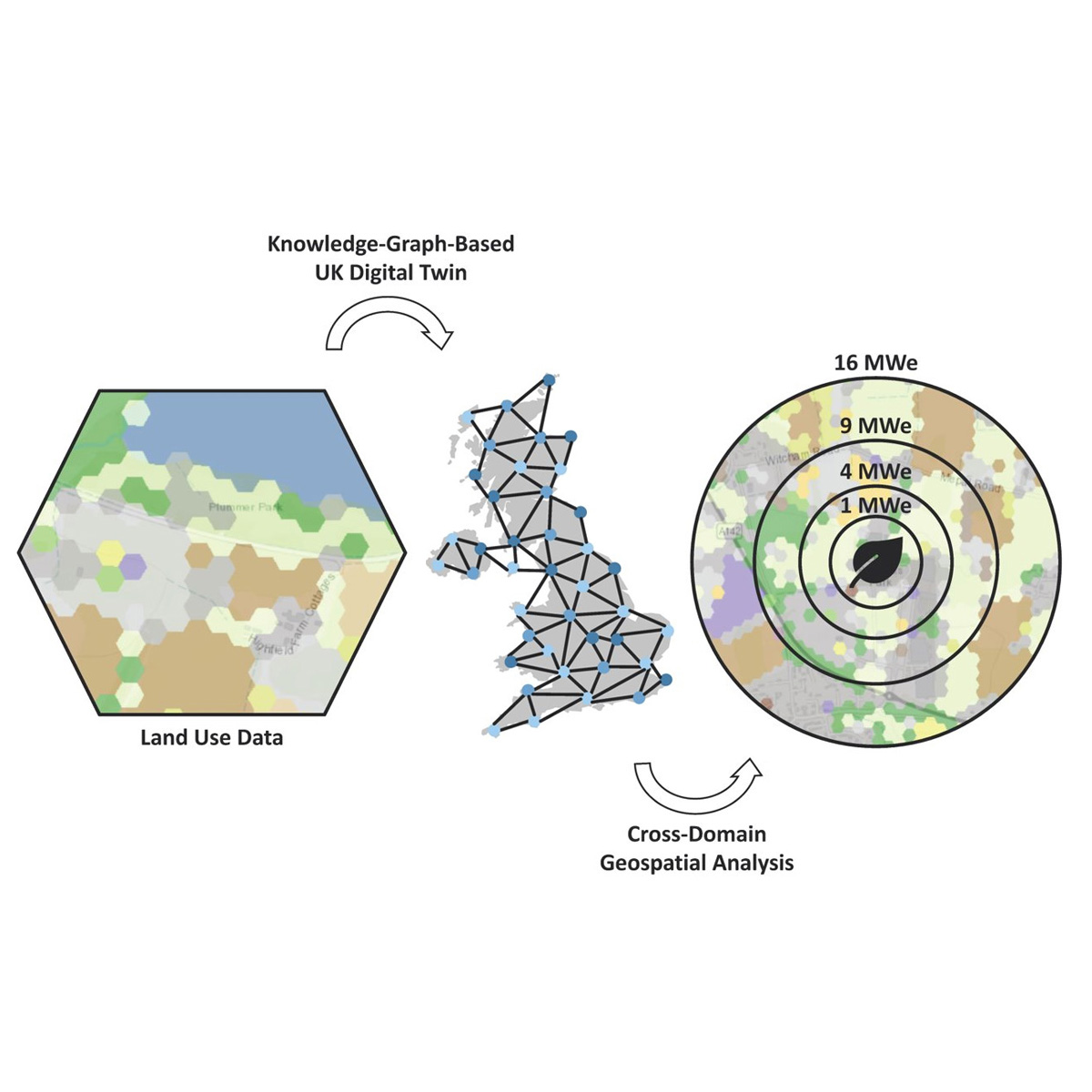
The Knowledge Graph based architecture of the Digital Twin allows the addressing of cross-domain geospatial questions. The image to the left shows an example that calculates how much land would be required to produce bioenergy at the Elean power station located in Cambridgeshire, UK. The power station was commissioned in 2000 and is fuelled using wheat, oilseed, and miscanthus. Biomass for the power station is sourced from within the vicinity of the plant. On completion, Elean was the largest straw-fuelled power station in the world with a capacity of 38 MWe and an efficiency of 32.5%.
Careful consideration must be employed when making decisions concerning land use and biomass resources. The 38 MWe capacity of Elean is enough to power 0.1 million homes. It is estimated that a wind farm located on the same land area as the crops used to generate power at Elean would generate 299 MWe, enough to power 0.7 million homes. Solar photovoltaics occupying the same area are estimated to be able to generate 1019 MWe, enough to power 2.4 million homes. It is estimated that if the land area used to grow crops consumed by Elean was instead used to grow food for humans, it would produce enough food for 59.8 thousand people. This highlights the ‘premium’ associated with using land to grow crops for bioenergy. The UK Digital Twin is designed to tackle exactly these types of question.
The map below shows a sample of the land use data in the UK Digital Twin for Cambridgeshire, UK. Adapted from “Universal Digital Twin - Land Use”.
 |
 |
 |
| CMCL Innovations cmclinnovations.com |
Computational Modelling Group como.ceb.cam.ac.uk |
Cambridge CARES cares.cam.ac.uk |